HSADab 2026
AI-Powered Modelling of HSA


Access the comprehensive database containing ~5,000 affinity data points. Updated with literature up to June 2024.
Explore complex structures generated by AI tools like DiffDock, AlphaFold 3. Filling the gap between affinity and structure.
Instant prediction of Binding Affinity and PPB. Powered by fine-tuned Large Language Models (LLM).
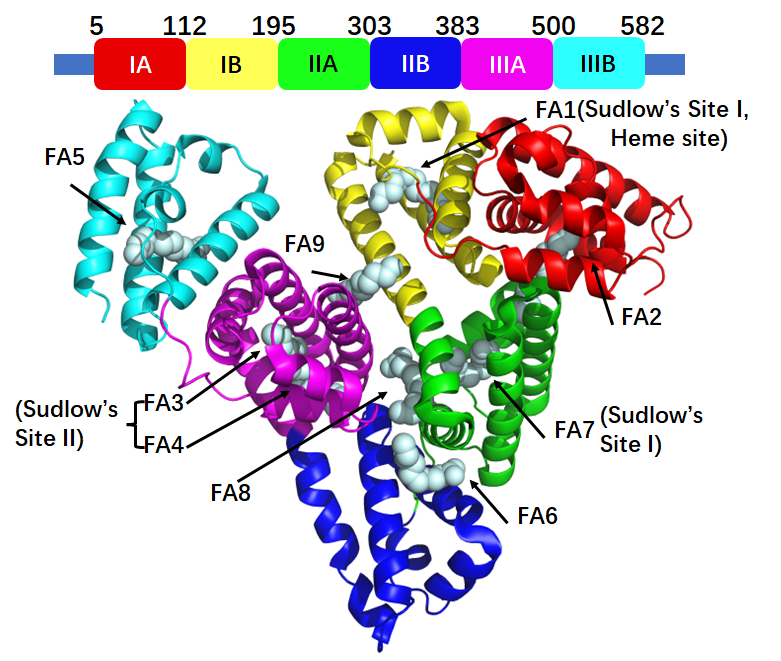
HSA is a complex protein composed of 609 amino acids, with a molecular weight of 66.5 kDa and a maximum circulatory half-life of up to 19 days in humans.
Structurally, its secondary formation includes 67% α-helix, 23% stretched chain, and 10% β-sheets. HSA features a heart-shaped globular conformation containing three homologous domains (I, II, and III). Crucially, HSA contains 9 fatty acid (FA) binding sites which are key for ligand interaction.
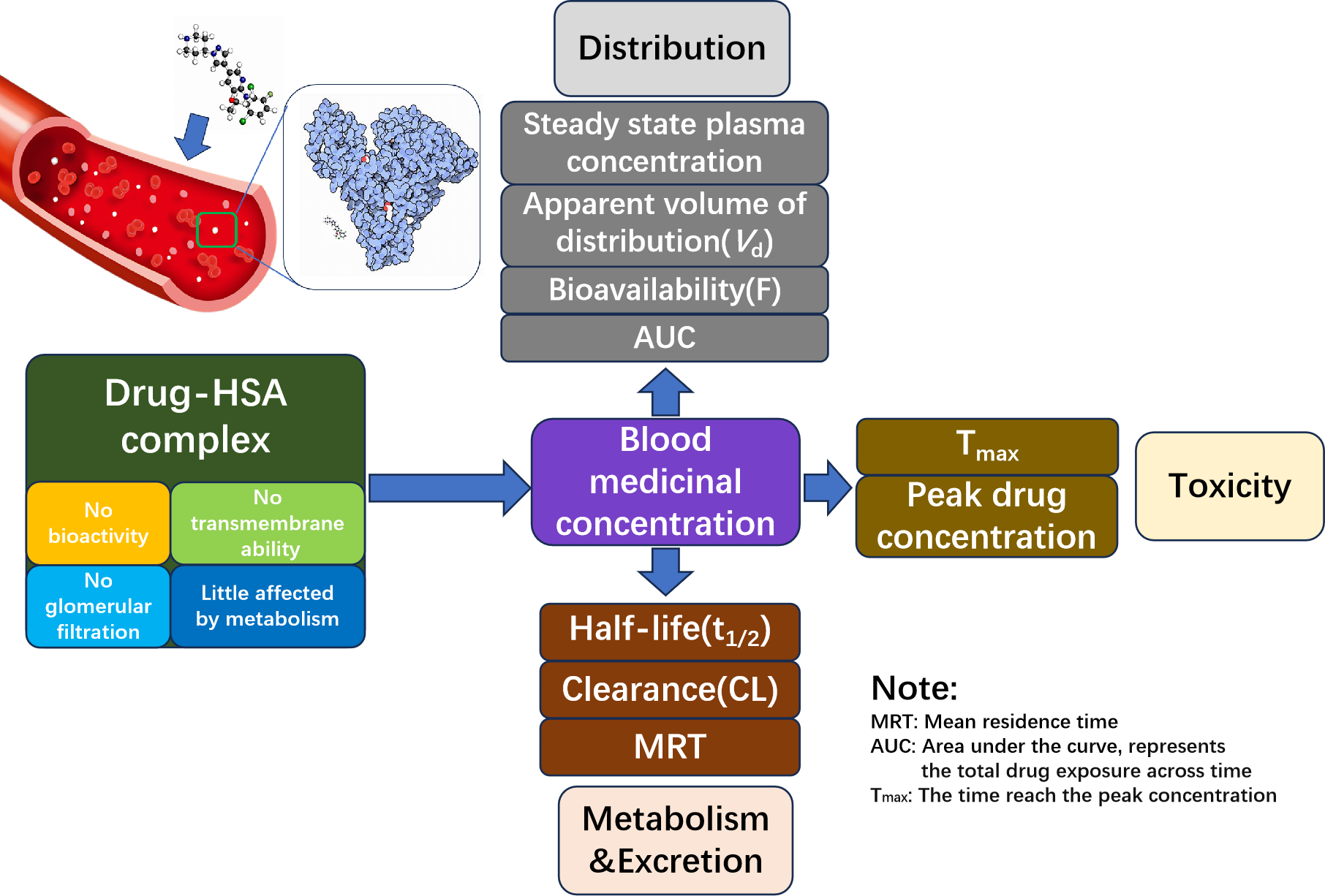
The interaction between drugs and HSA is magnificent in pharmaceutical distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADMET). When drugs are absorbed into the blood, HSA interacts with them, impacting their pharmacokinetics.
In the bound state, drugs typically show no bioactivity or transmembrane ability. This interaction influences the drug's half-life and peak concentration. Therefore, analyzing binding affinities on HSA serves as a proactive approach to predict the efficacy of preclinical drug candidates.